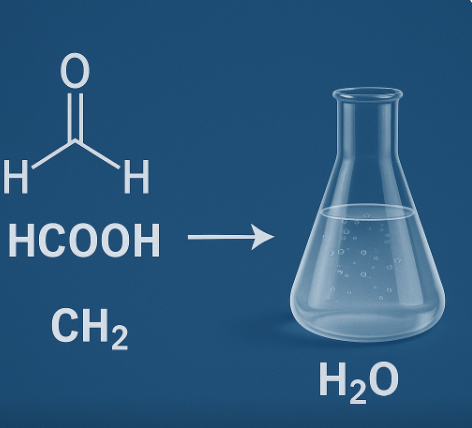
The combination HCOOCH CH2 H2O refers to a chemical interaction involving formic acid (HCOOCH), methylene group (CH₂), and water (H₂O). This combination is significant in organic synthesis, especially in reactions like hydrolysis, reduction, or decarboxylation. It’s commonly seen in laboratory pathways involving formylation or methylene transfer reactions.
Chemical Breakdown
-
HCOOCH (Formic Acid): The simplest carboxylic acid. Highly polar and reactive.
-
CH₂ (Methylene Group): A versatile carbon unit in organic reactions.
-
H₂O (Water): A universal solvent and often a reagent in hydrolysis or elimination.
How HCOOCH CH2 H2O Reacts
When HCOOCH CH2 H2O are part of a reaction system, formic acid typically acts as a reducing agent or acid catalyst, while water plays a role in hydrolysis or as a reaction medium. Methylene groups help in forming or modifying carbon chains. This trio contributes to mechanisms involving:
-
Hydroxymethylation
-
Methylene bridge formation
-
Oxidative cleavage or hydrolysis
Example Reactions Involving HCOOCH CH₂ H₂O
1. Reductive Methylation
Using formic acid and formaldehyde (CH₂O), methylation of amines occurs. Water assists as a medium:
2. Hydrolysis with Formic Acid
In ester hydrolysis, HCOOCH can assist in breaking ester bonds in aqueous conditions.
3. Biological Applications
This combination resembles pathways in formylation of biomolecules and detoxification mechanisms in cellular processes.
Why is HCOOCH CH2 H2O Important?
✅ Green Chemistry:
Formic acid is biodegradable and environmentally friendly, making the HCOOCH CH2 H2O system eco-conscious.
✅ Versatile Use:
Applies in synthetic organic chemistry, pharmaceuticals, and materials science.
✅ Simplified Mechanisms:
Makes complex transformations easier under mild conditions.
Real-World Applications
-
Drug Synthesis: Used in formylation and methylation steps.
-
Agricultural Chemistry: Supports synthesis of safer pesticide intermediates.
-
Food Science: Formic acid is used as a preservative, often in water-based formulations.
HCOOCH CH2 H2O in Industrial Use
Industrially, HCOOCH CH2 H2O is valuable in:
-
Producing resins and plastics
-
Facilitating biodegradable polymer chains
-
Catalyzing esterifications and formylations for bulk chemicals
Safety and Handling
-
HCOOH: Corrosive. Use gloves and ventilation.
-
CH₂ Compounds: Often gaseous or bound in reactive agents.
-
H₂O: Safe but essential in maintaining controlled conditions.
All handling must align with GHS safety protocols and lab SOPs.
Environmental Impact
This reaction system supports sustainable chemistry by:
-
Reducing reliance on heavy metals
-
Lowering toxic byproducts
-
Supporting green reaction pathways
FAQs
What does HCOOH CH2 H2O mean in chemistry?
It represents a reaction environment involving formic acid (HCOOCH), a methylene group (CH₂), and water (H₂O), commonly seen in organic transformations.
Is HCOOCH CH2 H2O safe?
Formic acid is corrosive. Methylene sources vary. Handle with PPE and proper lab safety protocols.
What is the role of H₂O in this reaction?
Water acts as a solvent or a reactant in hydrolysis and elimination processes.
Can this reaction be used in pharmaceuticals?
Yes. It supports key steps like reductive methylation or decarboxylation in drug development.
Is this considered a green chemistry pathway?
Yes. It reduces hazardous waste and uses biodegradable agents.
Conclusion
The HCOOCH CH2 H2O system plays a pivotal role in modern organic chemistry by providing a safe, green, and efficient route to synthesize a wide range of compounds. Its applications in industry, research, and green chemistry make it a topic of continual importance for chemists and environmental scientists alike.